GST registration is a transparent process that businesses & individuals must follow to comply with the country’s tax regulations.
In simple terms, GST is a consumption-based tax. It is applied to services and goods that you supply. When a business/individual offers services/ goods to customers, it collects GST on behalf of the government and remits it to the tax authorities.
Table of Contents
- What is GST registration?
- GST Registration in India
- What is GST?
- Objectives of GST
- When was the GST introduced?
- Types of GST Registration in India
- Benefits of GST Registration
- Documents required for GST registration
- Who should register for GST?
- What is Annual Aggregate Turnover in GST?
- GST Registration for E-commerce Businesses to Collect TCS
- How to do GST registration?
- How to check the status of GST registration?
- How to download the GST registration certificate?
- What is the penalty for not registering GST?
- Cancellation of GST Registration
- GST Registration Fees
- What is the GST Suvidha Kendra franchise?
- GST Suvidha Kendra: A Golden Opportunity for Business
- Some Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is GST registration?
Some Acronyms
RVAT: Rajasthan Value-Added Tax
GST: Goods and Service Tax
NRI: Non-Reliable Indian
SGST: State Goods and Services Tax
TDS: Tax Deducted at Source
CGST: Central Goods and Services Tax
TCS: Tax Collected at Source
OIDAR: Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval
IGST: Integrated Goods and Services Tax
LLP: Limited Liability Partnerships
ITC: Input Tax Credit
PAN: Permanent Account Number
KYC: Know Your Customer
OTP: One-Time Password
ISD: Input Service Distributor
UTGST: Union Territory Goods and Services Tax
MCA: Ministry of Corporate Affairs
2. GST Registration in India
In India, the Goods and Service tax was established in July 2017. Businesses with over Rs. 40 lakhs turnover must do GST registration. In exceptional category states like North-Eastern & hill states, the government has set the threshold limit of Rs. 10 lakhs.
This means any business whose turnover crosses the stated threshold needs to register for GST. In case of failure, businesses may have to face penalties. This could lead to serious legal consequences.
GST registration gives the privilege to businesses/ individuals to do GST collection from their customers. They can make a claim of the input tax credit for the services/ products they bought. Further, can become a legitimate & compliant taxpayer under the GST system.
Before we delve further, let us get a brief idea of GST.
3. What is GST?
GST is applied at each phase of the process (supply), from production to distribution. It is a type of indirect tax. This implies it isn’t paid toward the end buyer. It is gathered by organizations and afterwards passed on to the government.
4. Objectives of GST
- Was to create a simplified and unified tax structure
- Replace the earlier complex system of multiple indirect taxes
Let’s take an example to understand the simple GST Scenario:-
Imagine a shirt manufacturing process!
Here we will understand how GST is applied at each stage, starting from the cotton farmer to the final retail store
1. Cotton Farmer
The cotton farmer sells raw cotton to a yarn manufacturer for Rs. 1000. The GST rate is 5%, so the farmer charges Rs. 50 as GST and receives Rs. 1050 from the yarn manufacturer.
2. Yarn Manufacturer
The yarn manufacturer processes the raw cotton into yarn and sells it to a fabric maker for Rs. 1500. The GST rate remains at 5%. So, the manufacturer charges Rs. 75 as GST and receives Rs. 1575 from the fabric maker.
3. Fabric Maker
The fabric maker weaves the yarn into fabric and sells it to a shirt manufacturer for Rs. 2000. The GST rate is still 5%. So, the fabric maker charges Rs. 100 as GST and receives Rs. 2100 from the shirt manufacturer.
4. Shirt Manufacturer
Let’s say the shirt manufacturer cuts and stitches the fabric into shirts and sells them to a retailer for Rs. 3000.
The GST rate continues to be 5%. So, the shirt manufacturer charges Rs. 150 as GST and receives Rs. 3150 from the retailer.
5. Retailer
The retailer sells the shirts to the final consumer for Rs. 4000. The GST rate remains at 5%. So, the retailer charges Rs. 200 as GST and collects a total of Rs. 4200 from the consumer.
Calculation of GST at Each Stage:
| Vendor | GST Percentage | GST Applied (in Rs) | Final Cost |
| Cotton Farmer | 5% of Rs. 1000 | Rs. 50 | Rs. 1050 |
| Yarn Manufacturer | 5% of Rs. 1500 | Rs. 75 | Rs. 1575 |
| Fabric Maker | 5% of Rs. 2000 | Rs. 100 | Rs. 2100 |
| Shirt Manufacturer | 5% of Rs. 3000 | Rs. 150 | Rs. 3150 |
| Retailer | 5% of Rs. 4000 | Rs. 200 | Rs. 4200 |
Total GST Collected and Paid:
| Total | Divided Amount | Final Amount |
| GST Collected | Rs. 50 + Rs. 75 + Rs. 100 + Rs. 150 + Rs. 200 | Rs. 575 |
| GST Paid | Rs. 50 + Rs. 75 + Rs. 100 + Rs. 150 | Rs. 375 |
In this example, the final consumer pays Rs. 4200 for the shirt, which includes the total GST of Rs. 575.
However, the shirt manufacturer gets an input tax credit for the GST paid at the previous stages (Rs. 375).
So, the shirt manufacturer effectively pays only Rs. 200 (Rs. 575 – Rs. 375) in GST to the government.
This way, GST ensures that the tax burden is passed on at each stage of the supply chain, and there is no tax cascading.
The final consumer pays the GST which is ultimately shared by all the suppliers in the chain.
5. When was the GST introduced?
5.1 Simplification
Before introducing GST, there were many types of taxes. This includes service tax, sales tax, excise tax, etc. These taxes were levied by both state and central governments. Hence, created challenges for businesses because of the complicated tax structure.
With GST, the tax system is simplified. All taxes were integrated into one tax.
5.2 One Nation, One Tax
You might have heard this phrase very often. We have a unified tax system with it.
The same rules and tax rates are applied to services and goods across India. It reduced all the blockage that was related to tax and made it simpler for businesses to operate.
5.3 Eliminate Cascading Tax
Also, termed as a tax on tax. Businesses were fed up with cascading taxes. It was very hefty for them because taxes were applied at each stage of production & distribution. GST came into being to withdraw the cascading effect.
It promotes efficiency and reduces the overall burden of tax on businesses and consumers.
5.4 Boosts Economy
GST streamlined the tax structure and made it possible and efficient for businesses. This has helped many businesses to press forward in their operations. It also made things simpler for businesses that are new to entering the market.
5.5 Compliance and Transparency
The compliance system of GST was technology-driven. Hence, businesses can file tax returns online. It improves transparency and scope of tax evasion in the tax collection process.
5.6 International Trade
It made the taxation system of India more compatible with international practices. It facilitated and made Indian products more competitive in the global market.
6. Types of GST Registration in India
GST registrations depend on the business’s nature and its requirements. The different types of GST registrations are as follows:
6.1 Regular GST Registration
Most common GST registration type for businesses with a turnover of the specified threshold.
Rs. 40 lakhs for most states, Rs. 10 lakhs for special category states
Regular GST registration allows businesses to do the following:-
- Collect GST from customers
- Claim an input tax credit
- Carry out interstate transactions
6.2 Composition Scheme Registration
Small businesses with a turnover of up to Rs. 1.5 crores can try for this. Under this scheme, businesses can pay a lower GST rate and have less compliance burden.
However, they cannot call for input tax credits and are not allowed to engage in interstate sales.
6.3 Casual Taxable Person Registration
They are someone who undertakes taxable activities occasionally yet does not own a fixed place to do business. Such businesses must go for GST registration before doing any business activities.
6.4 NRI Registration
Any business that does not have business in India but supplies goods or services in India must go for this type of GST registration. They need to pay GST on the supply of goods or services and comply with the regulations applicable to them.
6.5 ISD Registration
Large businesses that have multiple locations within a state and wish to distribute the input tax credit among those locations need to register as an ISD.
6.6 TDS Deductor Registration
Certain specified entities, like government departments or public sector undertakings are required to deduct TDS on payments made to suppliers. They must do registration as TDS deductors, under GST.
6.7 TCS Collector Registration
The operators of E-commerce need to collect TCS from sellers on their platforms. They need to register as TCS collectors under GST.
6.8 OIDAR Service Provider Registration
Businesses that provide online services to customers located outside India are required to register under this category.
7. Benefits of GST Registration
7.1 Legal Recognition
GST registration provides businesses with legal recognition as suppliers. This will serve as evidence that your company is legitimate.
7.2 ITC
Any businesses that are GST registered can request Input Tax Credits for the purchases. This will be against the tax they have collected on sales. It will reduce overall tax liability and promote cost savings.
7.3 Inter-State Transactions
A business that is engaged with inter-state trade needs to get GST registration. With this, businesses can supply goods or services to customers. For interstate commerce, there will be no limitations.
7.4 Compliance and Credibility
With this registration, the company will comply with the regulations of tax. This enhances their credibility among customers, suppliers, and financial institutions.
7.5 Seamless Input Tax Credit Chain
With GST, there is transparency in the complete supply chain. This reduces the cascading effect of taxes.
7.6 Ease of Doing Business
GST simplifies the structure of tax and reduces compliance complexities. Once registered, businesses can manage their tax affairs more efficiently.
7.7 Nationwide Presence
GST is a single tax applicable throughout the country, replacing a multitude of state and central taxes. This creates a unified market and facilitates ease of goods movement across state borders.
7.8 Promoting Formalization
GST registration encourages businesses to become part of the formal economy, promoting transparency.
Overall, GST registration streamlines the tax system. It also promotes tax compliance and fosters economic growth. It simplifies tax administration for the government and contributes effectively to building a more robust and stronger economy.
8. Documents required for GST registration
8.1 PAN Card
A PAN card of the business or individual applying for GST registration is essential.
8.2 Certificate of Incorporation
Companies must share an Incorporation Certificate issued by the MCA.
8.3 Aadhaar Card
For individuals applying for GST registration, their Aadhaar card is required as part of the KYC process.
8.4 Proof of Address
Businesses need to provide valid proof of their principal place of business. Documents such as rent agreements, lease agreements, or utility bills (electricity bills, water bills, etc.) can serve as proof of address.
8.5 Proof of Appointment of Authorized Signatory
Details and proof of the authorized signatory of the business who will be responsible for GST compliance must be submitted.
8.6 LLP Registration Certificate/LLP Board Resolution
For (LLPs), either the LLP Registration Certificate or the LLP Board Resolution authorizing a designated partner should apply for GST registration.
Depending on the specific nature of the business and the state in which the registration is being sought, additional documents or information may be requested by the GST authorities.
Businesses and individuals should ensure they have all the necessary documents ready and accurate before initiating the GST registration process to avoid any delays or issues.
8.7 Bank Account Details
The business entity’s cancelled cheque or the account statement of the bank.
8.8 Authorized Signatory Details
It is mandated to present the identity and address proof of the person other than the business owner who is authorized to apply and sign GST registration.
8.9 Photographs
Passport-sized photographs of the business owner(s), partners, directors, or proprietors.
9. Who should register for GST?
The following categories of individuals and businesses should obtain GST registration:
9.1 Individuals Registered Under Pre-GST Law
This includes individuals or businesses that were registered under the previous indirect tax regime and have migrated to the GST system.
9.2 Exceeding Threshold Limit Businesses
The companies whose annual turnover outdo the financial year’s threshold limit must go for GST registration.
9.3 Casual/ Non-Resident Taxable Person
Any casual taxable person/ non-resident taxable person must do GST registration.
9.4 Agents of a Supplier & Input Service Distributor
Agents who make taxable supplies on behalf of a registered taxable person and Input Service Distributors are required to obtain GST registration.
9.5 Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) Payers
If you pay your tax under the RCM then it is necessary for you to do GST registration.
9.6 E-commerce Sellers and Aggregators
Sellers who supply goods or services through an e-commerce aggregator and the e-commerce aggregators themselves need to register for GST.
9.7 OIDAR service provider
Anybody who provides online details, retrieval, or database access services to India is required to do GST registration.
10. What is Annual Aggregate Turnover in GST?
The terminology “Aggregate turnover” as per the GST law pertains to the following:-
- Taxable supplies total amount (it excludes the inward supplies value on which an individual is accountable for tax payments via Reverse Change Mechanism.
- Exports goods/ services
- Exempt supplies
- Export services and goods (both)
- Individuals inter-state supply with the same PAN
This is calculated on the PAN India basis.. However, it excludes Integrated tax, State tax, Central tax, Union territory tax, or any other applicable cess.
As per the regulation of GST, the aggregate turnover (annually) is integrated turnover for the whole financial year.
This calculation is done at the PAN level. This involves summing up the following components:
- Exempt sales value
- Taxable sales value
- Export of services and goods
- Interstate stock transfers or supplies between distinct individuals using the same PAN and interstate supplies made by the business to its sister concerns
The calculation mentioned above does not include tax components like Cess, Integrated tax, State tax, Central tax, and Union Territory tax. Additionally, the taxable value does not take into account purchases where the person is obligated to pay tax under the reverse charge mechanism. Nevertheless, it’s important to note that sales subject to reverse charge remain part of the taxable supplies in the determination of the aggregate turnover.
The “Turnover in State” includes:-
- Total of all supplies that are taxable supplies.
- Exempt supplies that happen with the Union Territory or States
- Exports of services/ goods
- Interstate supplies that happen from the Union Territory or State by a taxable individual.
However, it excludes stock transfers and taxes such as CGST, SGST, UTGST, IGST, and cess.
For instance,
Let’s consider a case in a normal category state under GST. Mr A is an estate owner of a tea business with a turnover of Rs. 1.60 crores from the tea leaves sales. This is exempted from GST. In addition, Mr A supplies plastic bags separately and earns Rs. 5 lakhs from this transaction, which is taxable under GST. Therefore, his taxable turnover amounts to only Rs. 5 lakhs.
Considering the definition of “aggregate turnover,” Mr A needs to do GST registration because his turnover crosses Rs. 40 lakhs. He cannot go for the composition scheme because his turnover exceeds Rs. 1.5 Cr.
10.1 Special Category States under the Goods and Services Tax Law
The list includes the following:-
- Uttarakhand
- Tripura
- Nagaland
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Meghalaya
- Manipur
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Himachal Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- Assam
- Nagaland
- Tripura
- Mizoram
- Sikkim
- Ladakh
Notably, Rs. 40 lakh threshold limit is set for the regions like Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, and Assam for GST registration, while the other special category states have a threshold of Rs. 20 lakhs. The Union Territory of Puducherry also follows the Rs. 20 lakh threshold.
For instance, consider Mr B, a farmer residing in Nagaland. His turnover from agricultural activities amounts to Rs. 25 lakh, and his taxable turnover from selling plastic bags is Rs. 50,000. Even though the turnover is below the threshold, Mr B still needs to go for GST registration. It is because the turnover set for special category states is Rs. 20 lakhs.
As per the CGST (Amendment) Act, 2018, the Government, upon the request of a special category state and based on the recommendations of the GST Council can increase the aggregate turnover threshold from Rs. 20 lakhs to a maximum of Rs. 40 lakhs, subject to prescribed conditions and limitations. Consequently, the states of Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, and Assam had their threshold limit raised to Rs. 40 lakhs, while the other special category states continue to have a limit of Rs. 20 lakhs. This change took effect on 1st April 2019.
10.2 Threshold Limit
Below is a summary of different compliances under GST and their corresponding threshold limits based on aggregate turnover:
1. Normal GST Registration
The threshold limit for normal GST registration is the aggregate turnover in a financial year. If the threshold limit is crossed, then it is necessary to do GST registration.
2. GST Registration as a Composition Taxable Person
For opting for the Composition Scheme, the threshold limit is the aggregate turnover in the last financial year. If the annual turnover year does not cross the limit set, then they can go for the Composition scheme.
3. Applicability of e-Invoicing
The threshold limit for e-Invoicing applicability is the annual turnover in the preceding financial years starting from FY 2017-18. If a business’s aggregate turnover in any of the preceding financial years crosses this limit, it becomes liable for e-Invoicing compliance.
4. CA/CMA
The threshold limit for GST audit by CA/ CMA is the aggregate turnover during a financial year.
5. Eligibility for the Quarterly Return Filing under the QRMP Scheme
The threshold limit for eligibility under the Quarterly Return Filing and Monthly Payment of Taxes (QRMP) scheme is the aggregate turnover in the last financial year. Businesses with turnover below this stated limit can go for the QRMP scheme.
6. Mandatory HSN Code Reporting in Invoices
The threshold limit for mandatory HSN code reporting in invoices is the aggregate turnover in the previous financial year. If a business’s aggregate turnover in the previous financial year exceeds this limit, it must report HSN codes on invoices.
7. Levy of Tax in Case of Composition Scheme
The tax levied under the Composition Scheme is based on the “Turnover in the State.” This turnover refers to the turnover of an entity affected within a specific state or Union Territory.
These threshold limits are important considerations for businesses to determine their compliance requirements under GST. It helps in assessing whether they need to register, opt for specific schemes, or fulfil other GST-related obligations.
11. GST Registration for E-commerce Businesses to Collect TCS
GST registration forms and rules and structures for online sellers, online retailers, and online vendors to shift from normal or typical enrollment. Here, the online business administrator is subject to the arrangement of Duty Assortment at Source (TCS).
11.1 What is Tax Collected at Source (TCS) under GST?
Under GST, TCS refers to the tax collected by an online business it gets from the supplier’s services or goods who does supplies via the platform. A percentage of the net taxable supplies will be deducted from TCS. The arrangement of TCS under GST is managed under Section 52 of the CGST Act.
11.2 Who will do the TCS collection under GST?
Under GST, online business aggregators are responsible for tax deposits and tax collection. The rate is set at 1% for each transaction according to CGST Act Section 52. Traders or dealers who are selling goods or services online will get their payment after a deduction of 1% tax.
To claim the tax collected by the aggregators who are selling goods or services on platforms must go for GST registration. This would be even in the case their turnover is pretty less as stated in the threshold limit.
However, there are exemptions for suppliers of services who are not using an e-commerce operator to collect tax at source.
11.3 The Rules of GST Registration for those who are TCS liable
In addition, online business operators who are eligible under CGST Act Section 52 cannot go for a composition scheme.
According to this Section, all the companies with an e-commerce background must do GST registration. Anybody who is eligible for TCS collection must register for GST and fill out Form GST REG-07.
The companies can share their application to the GST portal. Else, they can get support from leading facilitation centres like GST Suvidha Kendra.
After submission of the application, the proper officer will verify the details and grant registration.
11.4 Rate applicable under TCS
The applicable rate under Tax Collected at Source is 1% of the transaction value. This rate is applicable to dealers or traders who do their business through e-commerce operators. The TCS amount is deducted by the e-commerce operator before making a payment to the dealer or trader.
For intra-state supplies, the TCS rate is 1%, which is divided into 0.5% under CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax) and 0.5% under SGST.
Similarly, for inter-state supplies (between different states), the TCS rate is also 1%, which is applied under the IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax) Act.
The rates are declared by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) in Notification No. 52/2018 under the CGST Act and 02/2018 under the IGST Act. Businesses involved in e-commerce transactions need to comply with these TCS rates while making payments and reporting their transactions under the GST regime.
11.5 Registration requirements under TCS provisions of GST
Under the TCS (Tax Collected at Source) provisions of GST, there are specific registration requirements for operators and sellers of online businesses supplying goods via portals.
Here are the registration conditions:
- E-commerce operators who are liable for TCS collection must do GST registration.
- Sellers supplying goods through an operator of an online business are also required to register under GST, except for specific supplies mentioned in Section 9 (5) of the CGST Act.
The exempt supplies listed in Section 9 (5) include services of transporting passengers by radio taxi and motorcycle, providing accommodation in hotels or guest houses for residential or lodging purposes, and house-keeping services (plumber, carpenter, etc.) by unregistered suppliers.
However, in these exempt cases, the e-commerce operator is responsible for paying GST and meeting the compliance requirements. Suppliers providing these exempt services do not have to register if their turnover does not exceed the threshold of Rs. 20 lakhs (or Rs. 40 lakhs for special states) for GST registration.
- Goods Suppliers who are selling via online platforms are not exempt from GST registration.
- An e-commerce company must register separately in GST for every state to which it supplies goods or services.
By adhering to these registration requirements, e-commerce operators and sellers can ensure compliance with the TCS provisions of GST and smoothly carry out their business activities in the online marketplace.
11.6 How can old stock be claimed for ITC?
Prior to the implementation of GST, any company with closing stock—whether or not it was registered—will be eligible to receive a credit for any tax that it paid. We will also discuss a few conditions that are dependent on this claim of ITC.
12. How to do GST registration?
It is quite easy and quick to do GST registration. You can go to the GST portal. Fill in the prerequisites asked in the GST REG-01 registration form.
- Go to the GST portal.
- Hit the tab “Services”, and then on “New Registration”.
- You will see an application form.
- Part A
- Part B
Part A
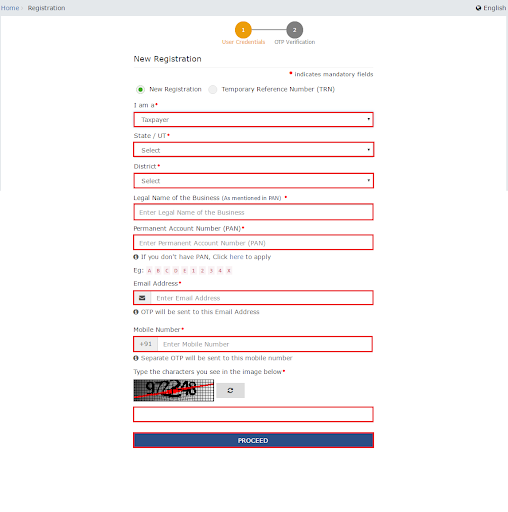
- Click on the dropdown under the header “I am a*” and choose “Taxpayer”.
- Next, similarly under the “State/ UI*” and “District” pick your location.
- Share the details in the input field of “Legal Name of the Business field (As mentioned in PAN)*”.
- Share your PAN number in the input field of “Permanent Account Number (PAN)*”.
- Share the email and phone number in the given field.
- Hit “Proceed” once you enter the CAPTCHA.
- Next, share the OTPs that you received on your phone number and email address.
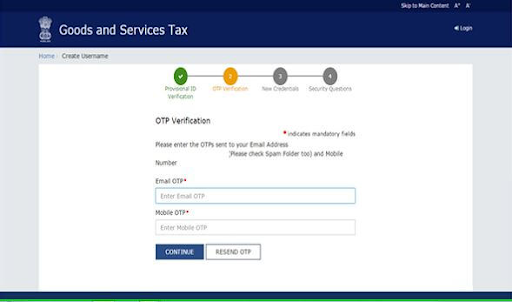
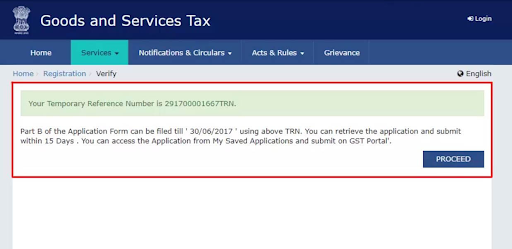
- Once you click the option “Proceed”, you will get the TRN number on your next screen. Jot down this somewhere.
- Check your phone number and email for the 15-digit TRN (Temporary Reference Number).
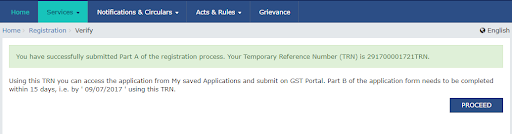
- Part A of the form is complete.
You get 15 days to complete Part B. So, ensure that you complete the application on time.
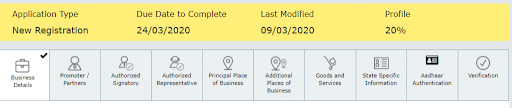
Part B
You need to complete 10 sections for Part B. Carefully fill in all requirements with the prerequisites asked.
List of things that you must keep in handy while going for GST registration for this section.
- Recent passport-size photographs
- Details of bank account
- Place of business proof
- Constitution of the taxpayer
- Aadhaar authentication and verification (if chosen)
- Next, under the section of Business Details, you need to share your trade name. Other than this, you need to share the district and constitution of the business location.
- Afterwards, you need to toggle the option “Yes/ No”. You will find this under the field Option for Composition.
- Post this, you need to choose the category type.
For instance, if you are a manufacturer then you need to click on the first check box. Read the instructions carefully and click your business accordingly.
- Tap on the declaration.

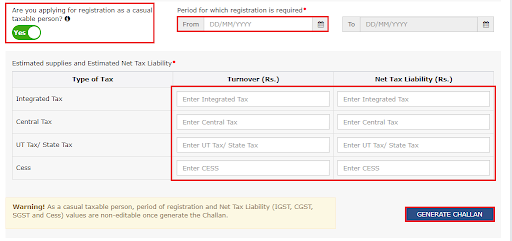
- Share the date of your business commencement and specify the date your liability has arisen. Choose “Yes/ No” for the registration type as a casual taxable individual.
- If you have opted for the option Yes, then you need to create the challan. For this, you need to enter the information for advance tax payment.
- You need to share your reasons to get GST registration. From the dropdown, choose Input Service Distributor.
Note:-
- For instance, if you choose an SEZ unit, you need to share the SEZ name, designation, order number of approval, etc.
- In the section of Indicate Existing Registrations, you need to choose your existing registration type. This can be Service, Tax, Central Tax, or Excise Tax. Then, you need to share the number and date of your registration. Later, hit Add.
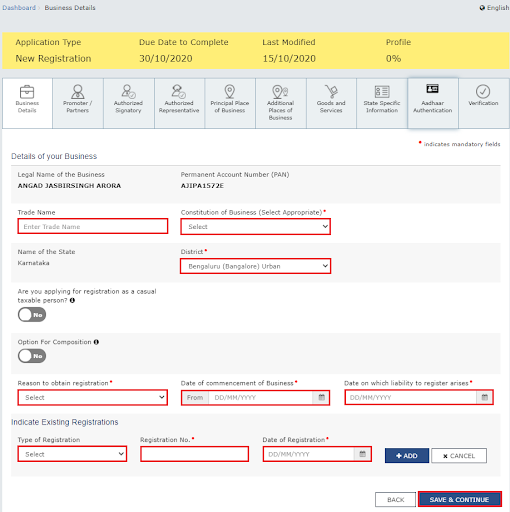
- The moment you complete the details, it turns BLUE colour. It denoted that the section (tile) is complete.

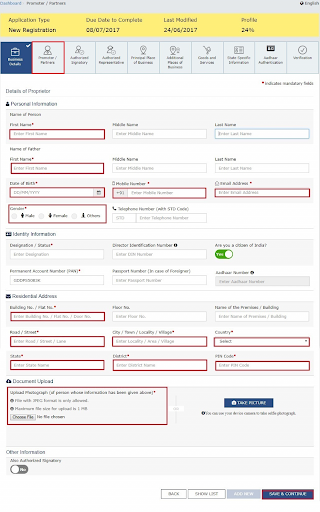
- Under the tile Promoters/ Partners, you can share the details of up to 10 Partners or Promoters. This will include personal information like Name, address, etc.
- You also may need to share the Directors’ Identification Number/ Designation or status. This will help to understand whether the taxpayer is a company, an Indian citizen, etc.
- Share the residential address and upload the stakeholder’s photograph. You can upload the image in JPEG or PDF format. The size of the file must be 1 MB.
- Hit the button Save & Continue.
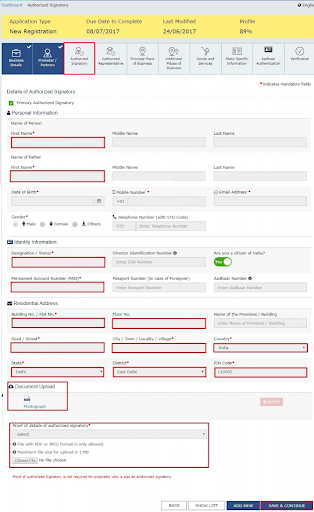
- Enter the Authorized signatory details. Follow the steps that you worked on in the previous steps. Click Save & Continue.
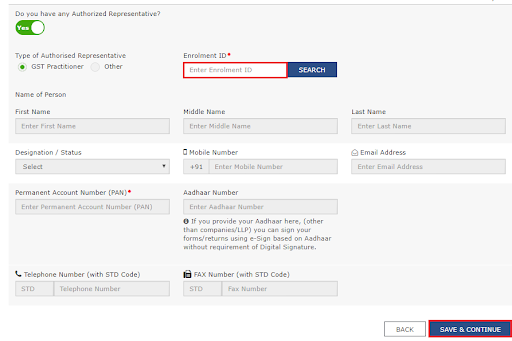
- In case you are a GST practitioner, you need to share the enrollment ID. You can share the basic details in case of authorized representatives. Click Save & Continue.
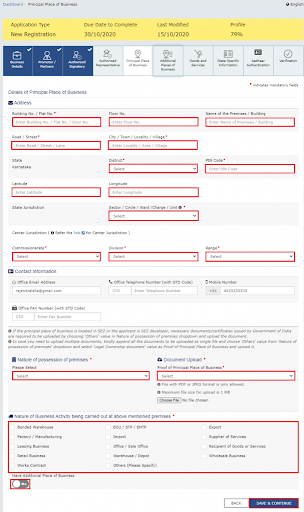
- In the case of entering the business’s principal place, you have to share the details aptly.
The primary location in the state where the taxpayer does business is the taxpayer’s primary place of business.
- Report the location, region, area/circle/ward/charge/unit, magistrate code, division code and reach code. Likewise, enter the authority contact number of the citizen and the idea of ownership of premises as leased or possessed or shared, and so on.
- Following up, transferring supporting records, remembering an assent letter or NOC for business for premises leased and transferring the verification of SEZ Unit/SEZ Designer endorsement for the premises, if pertinent. Likewise, mark the Idea of business exercises in the vicinity and add any extra business environments. Click on the ‘SAVE and Proceed’ button.
Notes:
- In case you are applying for GST registration as the IRP for the CIRP undertaking of the taxpayer company then you need to give the information of the taxpayer’s original registration.
- In case of uploading multiple documents, then you need to attach all documents in a single file and upload it. You can upload it in JPEG or PDF format and the maximum file size allotted is 1 MB. You can submit two files (max).
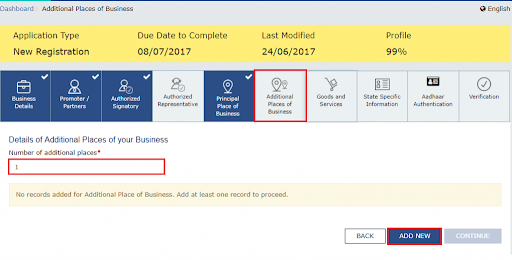
Share the details of services and goods in the next tab. You need to share it with SAC or HSN codes. You can share it for a maximum of 5 services/ goods.
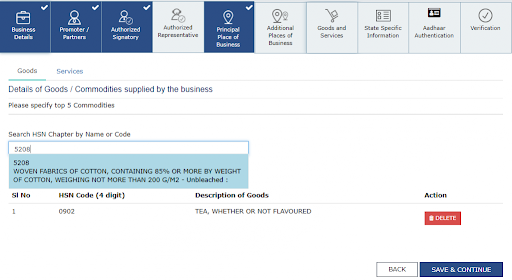
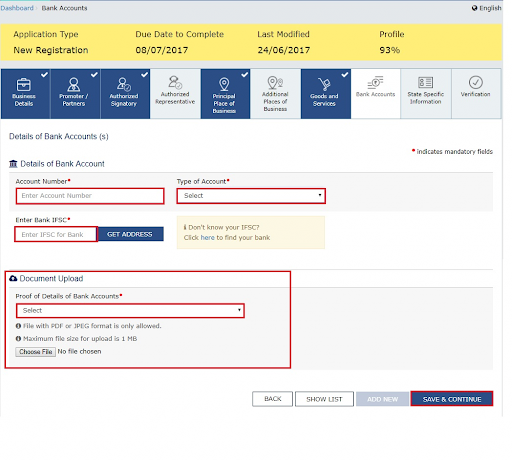
Next, share the taxpayer’s bank details. If you have not submitted these details in the initial phase of your GST registration, then you will get the prompt the moment you log in to the GST portal.
Also, ensure that you upload the supporting documents along with your details.
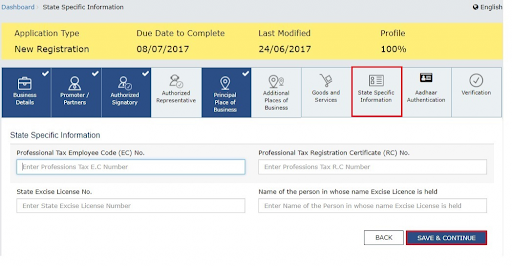
Under the tab of State Specific Information, you need to share the following:-
- Professional tax employee code number
- State Excise License Number
- PT registration certificate number
Finally, hit on Save & Continue.
You have to pick an option whether you want to do Aadhaar authentication or not.
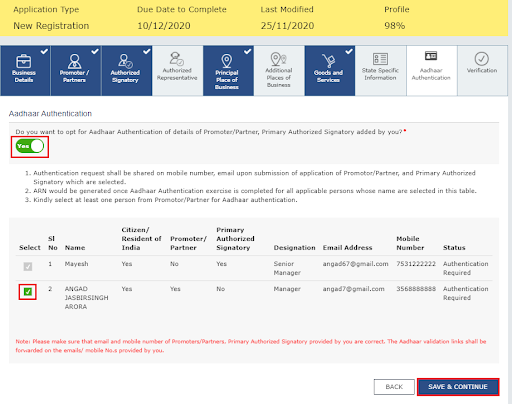
If in any case, the authorized signatory wishes to do Aadhaar authentication, then the officer may not do a physical verification of a site or premise. Please note that they may do so in special cases. The ARN will be generated immediately following that in such instances.
When you are done to finally enter the Verification page, you need to click on the checkbox for the declaration.
- LLPs and companies can use the option Submit with DSC to submit their application
- To submit with e-sign, you will get the OTP to your mobile number
- To submit using EVC, you will get OTP to your mobile number.
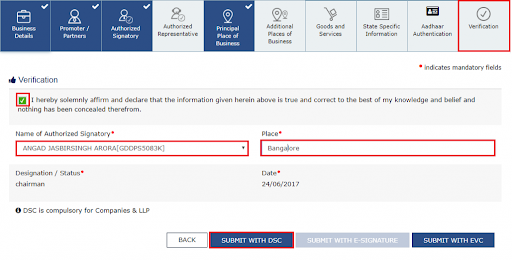
On successful application, you will receive the ARN number.
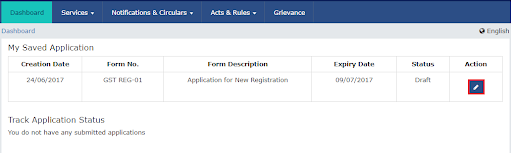
In case you are filling out the application on some other day:-
- Tap on the option “Services”, click “Registration” and then “New Registration”.
- Click on the option “Temporary Reference Number (TRN)”.
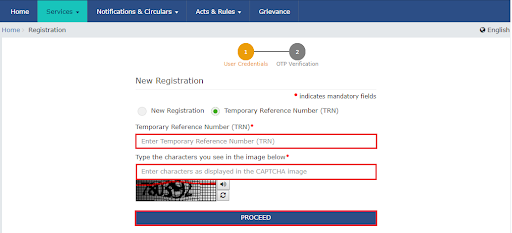
- In the input field, enter your TRN number and then CAPTCHA in the following field. Hit “Proceed”.
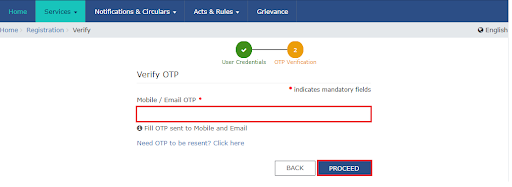
- On the next screen. Enter the OTP that you received on your email or mobile number and click “Proceed”.
- You see a page “My Saved Application”. Under the column “Action”, click on the 🖋️(edit) icon.
Note:-
Please follow the steps mentioned above to complete the steps for PART B GST registration
12.1 GST registration for individuals/ businesses who are supplying services from outside India
GST registration is required for businesses providing Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval (OIDAR) services from outside India.
Examples of OIDAR services include advertising on the Internet, providing cloud services (e.g., Google Drive), and offering e-books, movies, music, software, and other intangible products via the Internet (e.g., Amazon Prime Video), that supplies details via the computer network electronically, online gaming (e.g., Steam), and services such as sites like social networking, financial data, matrimonial, trade statics, etc.
Using the internet to facilitate service outcomes doesn’t automatically qualify as providing OIDAR services. Therefore, businesses offering OIDAR services to customers in India from outside the country are required to register under GST and comply with the relevant regulations.
13. How to check the status of GST registration?
- Browse to the GST portal
- Click on the tab “Services” and then the option “Track Application Status”.

- Pick the Registration from the dropdown.
Please note:-A first-time applicant is not applicable for the Refunds option.

- The moment you choose the option Registration, you will see ARN and SRN options. You can go for any option.
- For ARN
You will see the notification “Detailed Status: Show Case History of New Registration Application”. There are SEVEN stages.
The completed stage will be highlighted in GREEN. The pending GST registration will be in GREY.

13.1 Different stages of GST Registration status in ARN
- Pending for Processing
- Site Verification Completed
- Site Verification Assigned
- Clarification filed
- Pending for clarification
- Clarification not filed
- Approved
- Rejected
- For SRN
In case you go for the option, SRN- you will see “Detailed Status: Show Case History of New Registration Application SRN” As seen in ARN, the completed stage of GST registered status will be displayed in GREEN and pending in GREY.
Different stages of GST Registration status in SRN
- Pending with MCA
- COI (Certificate of Incorporation)
- COI issued by MCA
- COI issued by MCA
Hit on the hyperlink of ARN to get a detailed view of the GST Registration status. Tap on the tab Close when you are done checking your GST registration status.
On approval, you will get a USER ID as well as a Password. You can use these details and log in to the GST portal.
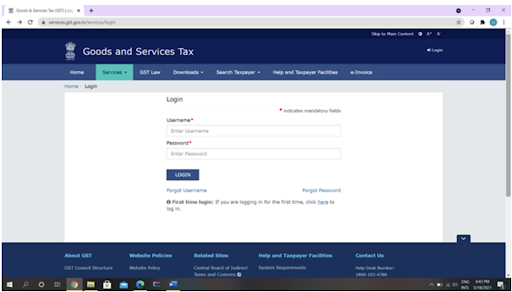
- Click on Login (Right-top) on the screen.
- Navigate to the option “First time login: If you are logging in for the first time, click here to login in”. Hit “here”, and you will see a prompt to open the window and download the certificate of your GST registration. The process may take 15 days.
Finding it hard to do GST registration? Speak to our experts.
14. How to download the GST registration certificate?
In the last step, we have seen the steps to download the GSTIN registration certificate. The moment you are allotted the GSTIN number, you must ensure to quote it on the invoices. You can also share this with your vendors and claim your input tax credit.
GST registration serves as proof of the taxpayer’s registration and compliance with the GST laws.
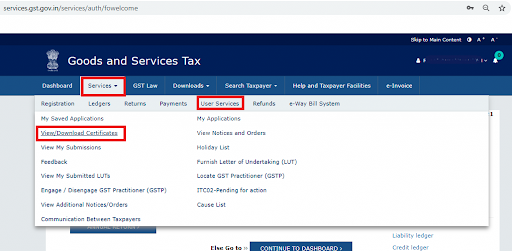
14.1 Steps to download the GST registration certificate
- Browse to the GST portal
- Browse to Services and then navigate to User Services.
- Click on the option View/ Download Certificate.
Next, tap on the icon of Download.
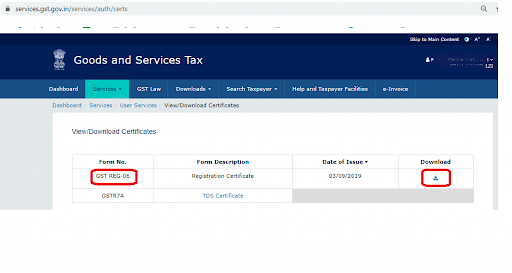
Take a printout.

Share the certificate in all your business places, be it UT or State.
GST Suvidha Kendra can help you to get the GST registration certificate in no time without any hassles.
14.2 Details contained in a GST registration certificate
1. Taxpayer’s Name and Business Details
The name, address, and other relevant information of the taxpayer or business entity.
2. GSTIN
A unique number assigned to the taxpayer upon registration under GST will be present on the certificate.
3. Date
The date when the registration happened.
4. Type of Registration
The type of GST registration. It can either be Regular, Composition Scheme, or any other category based on the taxpayer’s turnover and nature of business.
5. Validity Period
The period for which the GST registration is valid. Taxpayers need to renew their registration periodically as per the rules.
15. What is the penalty for not registering GST?
Some common penalties for GST registration-related issues include:-
15.1 Late Registration Penalty
If a business fails to do GST registration within the prescribed time limit, it may be liable to pay a penalty. This is calculated for each day of delay and is set for the maximum limit.
15.2 Incorrect Information Penalty
Providing false or incorrect details during the GST registration process can end up in penalties. If you provide any details that are misleading or inaccurate, then you may have to face penalties.
15.3 Non-disclosure Information Penalty
If you fail to disclose details like turnover details/ additional business location while doing GST registration, you may attract penalties.
15.4 Failure to Update Information Penalty
You must make sure to update your GST registration promptly otherwise you will be penalized.
15.5 Non-maintenance of Records Penalty
As a registered taxpayer, you need to ensure that you maintain complete and accurate records of transactions. Else, you will be penalized.
15.6 Non-filing of GST Returns Penalty
You need to pay your GST Returns on time. In case you do not make your payment within the said due date then you may be charged a penalty.
16. Cancellation of GST Registration
1. Voluntary Surrender
Businesses that wish to voluntarily exit the GST system can apply for cancellation of GST registration.
2. Death of the Proprietor
In the case of a sole proprietorship, if the proprietor passes away, the legal heirs or representatives may apply for cancellation of the GST registration.
3. Amalgamation or Merger
If a business entity undergoes amalgamation or merger with another entity, you can apply for the cancellation of GST registration.
4. Reduction in Business Scope
If a business changes its scope and no longer falls under the GST ambit, it may apply for GST deregistration.
16.1 How to cancel GST registration?
- Navigate to the GST Portal
- Go to the “Services” Menu.
- Choose “Cancellation of Registration”.
- Under the “Services” menu, click on the “Cancellation of Registration” option.
- Complete the application. Also, share the reason for cancelling the registration. This will include turnover details if the reason is turnover below the threshold.
- Submit the cancellation application. You will get ARN. This you will receive on the registered email and mobile number.
The authorized person will verify the details that you have shared. They will approve your application if everything is right.
You will get your cancellation order once your application is approved.
Please Note:-
Even after the cancellation of GST registration, you may be required to file pending GST returns. You need to pay any outstanding taxes (if applicable).
16.2 How does an e-commerce operator cancel GST registration?
The officer will conduct a proceeding or inquiry to check if an individual is eligible or not for TCS collection. If they are not eligible then the officer will cancel the registration.
This information will be notified via FORM REG-O8 electronically. The process that is given in the CGST Rule 22 will be processed.
17. GST Registration Fees
There are no GST registration fees specified under the law of GST. It is a tedious task to do GST registration. It involves scanning plenty of documents and entering details. The server issues are another problem-makers that can delay your registration process.
Visiting the nearest GST Suvidha Kendra Franchise will be the wiser option.
18. What is the GST Suvidha Kendra franchise?
A GST Suvidha Kendra is an authorized center or service provider appointed by the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN). They are authorized to open the GST Suvidha Kendra franchise. These centres act as intermediaries between taxpayers and the GST department, making it easier for businesses to comply with GST regulations.
Here’s how a GST Suvidha Kendra can help with GST registration:
1. Expert Guidance
GST Suvidha Kendra staff are well-trained and knowledgeable about GST registration requirements.
2. Document Collection and Verification
GSKs can help businesses gather and organize the required documents for GST registration.
3. Support with Digital Signature and EVC
If the registration application requires a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or Electronic Verification Code (EVC), GSKs can help businesses with the authentication process.
4. Prompt Communication
GSKs act as a point of contact for businesses with the GST department. They make sure that there is timely resolution and communication for issues or queries that may happen during the process of GST registration.
5. Additional Services
Apart from registration, GST Suvidha Kendras may offer other services, such as return filing, invoice generation, and reconciliation, making them a one-stop solution for business needs.
Engaging the services of a reliable and authorized GST Suvidha Kendra can be beneficial. This is especially for businesses and individuals with limited knowledge of GST processes or those seeking assistance to navigate the registration requirements smoothly.
19. GST Suvidha Kendra: A Golden Opportunity for Business
Setting up a GST Suvidha Kendra franchise can indeed be a promising business opportunity. Here are some factors that make it a potentially lucrative venture:
1. High Demand for GST Services
GST compliance is essential for all registered businesses. Many seek assistance to navigate the complex GST procedures. As a GST Suvidha Kendra, you can cater to this demand by offering a range of GST-related services, such as registration, return filing, etc.
2. Authorized Service Provider
Becoming an authorized GST Suvidha Kendra means that you are authorized to provide these services. This official recognition can instil trust in your potential clients and enhance your credibility in the market.
3. Wide Customer Base
GST Suvidha Kendra is a known name in the market. There are many that find it challenging to handle GST compliance on their own.
4. Recurring Revenue Model
GST compliance is an ongoing process, with regular return filing requirements. Hence, you can easily build a steady stream of recurring income. In addition, you can earn great commissions.
5. Technology-Driven Solutions
Utilizing technology and software tools can streamline your service offerings and make GST compliance more efficient for your clients. Automating processes can enhance your service quality and attract more customers.
6. Networking Opportunities
As you engage with various businesses through your GST Suvidha Kendra, you have the opportunity to build a strong network of clients.
However, like any business venture, setting up a successful GST Suvidha Kendra requires careful planning, investment in technology and infrastructure, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Seek professional advice and consider obtaining the necessary licenses and permissions to operate as a GST Suvidha Kendra. With the right approach and commitment, this business opportunity can be rewarding and financially viable.
Want to sell GST registration in your area? Click here.
20. Some Frequently Asked Questions
How to check if GST applies to my business?
GST is applicable for any business that has Rs. 20 lakhs annual turnover. In case you do your business in the Northern Eastern States like Mizoram, Assam, Tripura, Manipur, Nagaland, Meghalaya or Arunachal Pradesh the threshold limit is set for Rs. 10 lakhs.
A similar limit is also set for hilly regions such as Sikkim, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand, and Himachal Pradesh.
I do travel and tourism business in Assam with a turnover of around Rs. 8 lakhs. Should I do GST registration?
The GST registration limit for the hilly and Northern Eastern states is Rs. 10 lakhs. Since your annual turnover does not cross the specified threshold limit. Hence, you do not need to do GST registration.
Please note, Expert'ses registration is mandated in the following cases.
- For claiming the input for the paid tax on purchase from the supplier.
- If your supplier is GST registered and is willing to claim his credit on the purchase he made. This supplier can only do this when you issue a GST invoice. Hence, it is necessary to do GST registration in Expert'se.
I am running a departmental shop in Rajasthan. I have already registered my business under RVAT. Do I need to do a fresh GST registration?
An existing taxpayer gets transitioned automatically to GST. This simply denotes that you will be considered for GST registration. In the initial phase, you will be allotted a provisional registration ID. As per the government norms, this is then replaced by the Final Registration ID.
Who are existing taxpayers?
Any existing taxpayer was registered under Central or State laws. This includes Service Tax Act, Central Excise Act, and Value Added Tax Act.
- Entertainment tax
- Luxury tax
- VAT or State Sales Tax
- Central Excise
- Entry Tax
- Service Tax
Do I need to have a PAN card to apply for GST registration?
Yes, a PAN card is a must to apply for GST registration. NRIs are exceptional. They can use other documents to get GST registration.
I had settled for the Composition Tax Scheme earlier. Will the Composition Scheme concept still be there under GST?
Yes, it will be. Businesses with Rs. 75 lakhs annual turnover or less than that can avoid GST collection and can opt for the Composition Levy.
Has the Government set any time limit for GST registration?
Indeed, GST is pertinent since April 1, 2017.
The following deadline must be adhered to:-
Currently, the vendor who is registered without a new application will get a Provisional ID. This can be changed with the Final GSTIN number on the formalities completion.
I am planning to get my business registered in numerous areas inside Maharashtra. Do I have to apply for GST registration independently for every area?
In case you are planning to start your business in multiple locations in the same state then you can get all those businesses in a single application of GST registration. You can add any business location as your primary and add the others in the additional section.
The government has set no limit for the business branches.
Who is NRI in GST?
If you occasionally provide goods or services as an agent, principal, or in any other capacity where GST is applied (in taxable territory), but do not have a physical location in India, you will be considered an NRI in GST.
There are some key points that you need to consider as an NRI:-
- The registration will only have validity for 90 days.
- Validity for 90 days can be extended.
- You need to make an advance tax deposit for the registration period. This additional tax must only be deposited if your registration extension is sought.
- The deposited tax can be employed as an “?input credit?”.
How might business returns be documented under GST Regulation?
As per the law of GST, a taxpayer needs to furnish one annual and three monthly returns. Likewise, there are independent returns for a citizen registered under the composition scheme. The due dates to file returns are as follows:-
For the months of August and July, you need to file GSTR 3B.
Is it mandatory to use DSC to sign the registration application electronically?
Yes, it is mandatory for businesses to use DSC to sign the registration application electronically. It is essential for companies that fall under foreign companies, Foreign Limited Liability Partnerships (FLLPs) and LLPs (Limited Liability Partnerships.
In case you do not fall under these categories, then you can use DSC as an option to sign the registration application electronically.
I have my business in two different states (Kerala and Maharashtra). Do I need to do two separate GST registration?
Yes, you must apply for two separate GST registration for your business. It will be even applicable in the case where the business PAN is the same.
I sell my products via an online portal. Do I need to do GST registration?
Yes, you need to do GST registration. The government has made it compulsory for businesses that are rendering their service or selling their products via e-commerce operators such as Ola, Flipkart, Amazon, etc.
I have my business registered under GST. How can I avail Input Tax credit on goods that are duty paid, lying as stock on 30th June? In addition, I have shown the VAT returns in the ITC balance. Will my amount be carried forward to GST or will I get a refund for the same?
Tax credit for the laws of pre-GST such as excise, VAT, etc. You can carry forward the amount by filing the forms of transition (Tran 1 & Tran 2).
Who can go for Composition Scheme as per the GST law?
Small taxpayers can go for the composition scheme. They can simply avoid the tedious formalities of GST and pay GST at the fixed turnover rate.
Anybody who has a turnover of less than Rs. 1.5 crores can go for this. In the case of businesses from hilly states and North-Eastern states, the turnover should be less than Rs. 75 lakhs. The service providers with an aggregate of up to Rs. 50 lakhs can go for the Composition scheme.
What threshold limit should be considered for my business turnover?
The aggregate turnover is considered for the calculation of turnover. The terminology of Aggregate Turnover in GST denoted the taxable supplies' aggregate value. This will exclude the inward supplier who is a reverse charge liable. But it will include exempt supplies, exports of both, or either services or goods and inter-state individual supplies having the same PAN, must be mobilized PAN-India. Please note that you need to exclude IGST, UTGST, SGST, CGST and cess must be excluded while making the calculation for aggregate turnover.
How much time should I wait to register my business under GST?
Any business or individual must ensure to do it within 30 days before they become liable.
What should I do if my GST registration application gets rejected?
In case your GST registration application gets rejected, then you get the option to respond to the rejection letter. You can share your feedback and requests. If you plan to get a new GST registration application then you need to wait for at least 10 days for the final rejection notice.
What should I do once I get GST registration?
Once you successfully obtain GST registration, you will get a GST registration certificate with a GSTIN number enclosed in Form GST REG-06. One will be qualified to raise invoices that are GST-complaint and avail input tax credit. You must initiate filing GST returns quarterly or monthly.
Do I have to make a payment to get a GST number?
Obtaining a GST or GSTIN number or doing GST registration will not cost you anything.
What are the advantages of doing GST registration?
A. Normal taxpaying business
- Manage interstate business without any restrictions
- Get an input tax credit
B. Composition scheme vendors
- Less liability of tax
- Limited compliance
- Less impact on working capital
C. Business voluntarily opted for GST registration (Annual Turnover below 40 lakhs)
- Manage interstate business without any restrictions
- Get an input tax credit
- Competitive advantages
- Register e-commerce and other online website easily.

